Unlock Expert Advice with Zero Commitment.
We’ve Eliminated the Barriers.

HIPAA compliance is mandatory for all organizations involved in healthcare and handling medical data. As a global custom software development company, we know the importance of building HIPAA compliant software. But very few people associated with the healthcare industry know even the basic rules of HIPAA. Consequently, we thought of writing an exhaustive blog to be used as a reference point for all HIPAA-related queries.
For the uninitiated, HIPAA stands for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. But why is it critical? What role does it play? Knowing all this is essential because of its associated statutory and legal consequences. Did you know that even a tiny HIPAA offense results in penalties for the healthcare provider? You could be fined between $100 and $50,000 or even jailed for it, resulting in a loss of reputation. With such consequences, it is better to understand what is required for HIPAA compliance and adhere to it from the start.
Formulated in 1996, HIPAA lays down a set of healthcare regulatory requirements. They define how healthcare providers and health insurance companies must protect and safeguard sensitive and confidential patient data. The Health and Human Services (HHS) Department regulates this compliance while the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) enforces its provisions.
HIPAA was primarily designed to curb the flow of confidential information in the healthcare sector. By limiting access to PHI or Protected Health Information, HIPAA seeks to prevent its misuse. The HIPAA Act covers all healthcare providers, clearinghouses, and insurance providers. Entities associated with them also come under the purview of this Act.
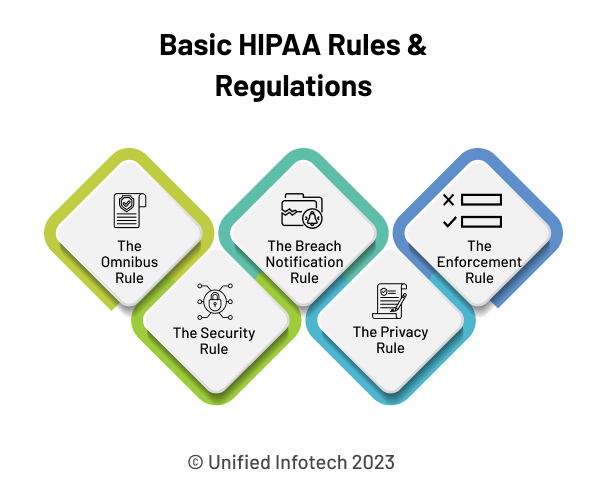
HIPAA comprises the following essential components that define its implementation, usage, and non-compliance procedures.
These primarily focus on the security of PHI as required for integration during HIPAA compliant software development. Protected Health Information or PHI includes a patient’s mental and physical health and personal data, including social security numbers etc. It also consists of the type of treatment provided to the patient and how the payment was made.
The HIPAA Privacy Rule seeks to educate patients about their PHI protection rights. It also allows patients to seek their health records and provide data corrections if required. As a special provision, the Privacy Rule also permits the use and disclosure of a patient’s health records. But this can only be used for enabling patient care and other justifiable purposes.
This rule deals with the methods that need to be implemented to ensure the integrity of ePHI and enable its protection. All involved entities should proactively anticipate ePHI-connected risks and implement ways to eliminate them. Further, these implemented protection methods must be regularly reviewed and modified.
There are many healthcare companies that knowingly or unknowingly fail to comply with HIPAA software requirements. What rules should govern these HIPAA breaches? All these are defined in this portion of the security-centered HIPAA Act.
Appended to the original Act in 2013, this rule makes it mandatory for all healthcare entities and businesses to be HIPAA compliant. Rules governing the formation and execution of Business Associate Agreements or BAAs are also mentioned here. Constructing the BAA is a requirement for sharing and transferring PHI or ePHI. Related fines and penalties to be implemented due to the breach or non-compliance of the Omnibus Rule are also mentioned here.
This rule deals with the workings of the HHS and OCR. It defines the steps they should take to ensure the implementation of this Act. Procedures for conducting non-compliance investigations and hearings are also mentioned here. It also defines how the related penalties will be calculated.
Often, businesses associated with the healthcare industry fail to implement HIPAA compliant software provisions due to ignorance. They make mistakes that can be easily avoided with a little knowledge and diligence. Some of the errors most healthcare industry members and their associates commonly make include:
Failure to comply with HIPAA regulations is enough for penalties to be levied. There is no need for the involvement of an active PHI breach. All intentional or unintentional violations of the HIPAA IT compliance requirements can be divided into four tiers. This division takes into account the severity of the violations and their impact.
Sometimes HIPAA violations can also result in lawsuits being filed and criminal consequences. The penalties associated with a plausible HIPAA violation are very high. Hence ensuring HIPAA compliance for software development is extremely important.
Along with healthcare providers, clearinghouses, and insurance providers, even associated software vendors must be HIPAA compliant. They should understand its requirements and implement them in their custom software solutions.
According to HIPAA rules, all software solutions that either process, store, or transmit patent data electronically need HIPAA compliance. HIPAA spells out precise instructions for classifying software as HIPAA-compliant. These include:
Following these instructions will help custom software developers guarantee the integrity, confidentiality, and accessibility of PHI; the core requirement of the HIPAA Act.

Let us now define the entities and businesses that fall under the purview of HIPAA. The healthcare providers mentioned in HIPAA’s context include:
The classification, Health plan providers primarily include insurance companies and health maintenance organizations. Private and public organizations that pay for the healthcare services rendered to respective insured patients also come under its purview.
By Healthcare clearinghouses, HIPAA refers to those institutions and facilities that process financial transactions related to billing, claim processing, etc.
HIPAA also applies to all business associates of healthcare service providers, health plan providers, and clearinghouses. The only criterion is to render services involving patient health information.
Other than being a statutory requirement, HIPAA compliance also benefits healthcare industry businesses by:
All businesses and entities involved in the healthcare industry in any capacity need to follow a hipaa compliance checklist for software development. This will automatically ensure HIPAA adherence, leaving healthcare business owners free to leverage the above benefits and generate commercial profits.
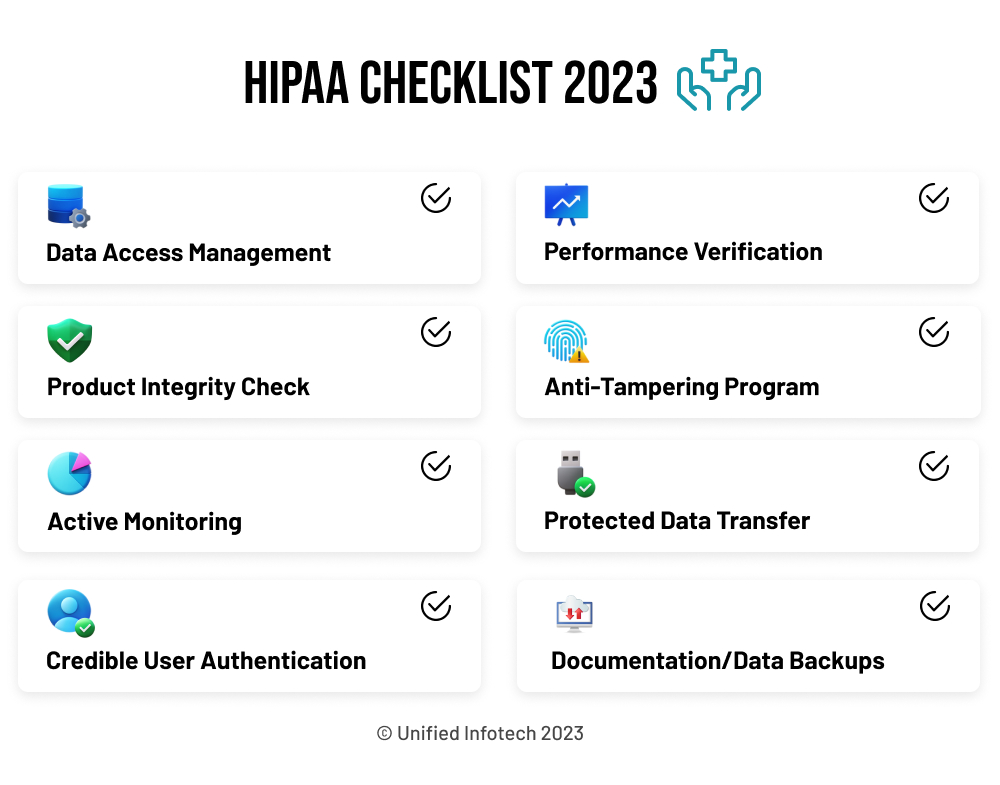
HIPAA consists of specific basic rules that all healthcare companies must adhere to. It requires the implementation of certain technical and administrative or non-technical safeguards for its compliance. With so much to take care of, preparing a HIPAA compliance software checklist helps keep things in perspective. Let us explore some points that this checklist must cover.
The healthcare industry is increasingly progressing towards digital consultations and online evaluations. But are these processes in sync with the HIPAA Privacy Rules governing the security of the PHI and ePHI? This is something that healthcare professionals have to ensure.
Privacy of PHI is also closely linked to the security protocols defined in the HIPAA Security Rules. Healthcare providers must study these rules minutely and implement the required measures to avoid HIPAA violations.
By analyzing the HIPAA Privacy rule, healthcare industry officials can understand patient data types that need protection. It also defines the different degrees of access required to assess PHIs. Gaining the right insights will enable healthcare providers to implement the required security and privacy measures. Some critical patient information that needs protection within the HIPAA compliant software include:
We have already discussed the possible HIPAA violations and the fines/penalties associated with them. Let us explore this in-depth here so that healthcare providers and associated entities can mitigate the chances of making these violations.
Healthcare providers need to understand that a data breach is not restricted only to external hacks. HIPAA defines a data breach as any PHI/ePHI access that does not have the required authorizations. So along with cybersecurity practices, strong internal security practices must also be set up to prevent this.
Additionally, recognizing common violations can also help healthcare providers prevent such instances from occurring. Some HIPAA violations that are pretty common include:
Please note that minor HIPAA breaches must be corrected immediately. But all major breaches must be reported to the relevant HIPAA authorities within 60 days of their occurrence.
HIPAA regulations are frequently updated based on the data security requirements of the changing times. Consequently, a healthcare software development company must be extremely vigilant about all announced HIPAA updates and implement them in their HIPAA compliant software.
The more healthcare providers document their HIPAA compliance measures, the better the chances of mitigating instances of non-compliance. Data needs to be regularly backed up and stored securely on the platform. Conduct regular audits to check for their integrity and availability.
Regularly implement mechanisms to audit user activity and access to PHI. These proactive audits will help detect anomalies related to a possible security breach in their initial stages. Maintain audit logs to record all PHI access user activities.
Enhance the effectiveness and functionality of HIPAA compliant custom software by integrating the below-given features.
Achieve this effectively by implementing auto log-off mechanisms, ensuring compliance with encryption standards, and establishing emergency access protocols.
Track and record all successful and unsuccessful attempts of data access. Maintain a record of all modifications made to the stored data. Also, limit access to all log files.
Separating the system infrastructure into data and system layers will enhance the integrity of the developed HIPAA compliant software.
Achieve this by implementing security measures like digital signatures, encoding, and blockchain solutions.
Applying multi-factor authentication is a must. Limit user access to authorized personnel only and block all compromised or suspicious accounts.
Use only encrypted communication protocols. It is also essential to verify the transmitted data’s integrity and block all non-secure communications.
Every software development company needs a good understanding of HIPAA to build quality HIPAA compliant software. We ensure HIPAA software compliance at every stage of the development process. Read on to understand how we ensure HIPAA compliance.
We collaborate with our healthcare clients and define the project’s core aims. We analyze this to determine all the features to be integrated and define estimated delivery timelines. This comprehensive approach helps us design a solution that closely meets the requirements of our healthcare clients.
In this phase, we analyze and determine the HIPAA compliances our healthcare clients must adhere to. Then we integrate them into our project plan draft.
Here, we take special care to ensure the website design does not violate HIPAA privacy rules. We excel at ensuring the seamlessness of our custom-developed software so it can offer a great user experience.
At this stage, we implement all the above-mentioned best practices for building HIPAA-compliant software. We also test all the HIPAA compliances we have integrated into the software to ensure there is no slack in their execution.
When we deploy the software, we ensure it integrates flawlessly with existing healthcare modules without causing disruptions. We also offer intensive post-deployment support because the nature of the healthcare industry demands it.
We build robust, resilient, and secure HIPAA compliant software by following the earlier steps. Conducting extensive software audits frequently helps check the viability of integrated security measures. We also keep track of all amendments and updates to the HIPAA rules and regulations and implement them into the HIPAA compliant software we build.

We’ve Eliminated the Barriers.
We stand by our work, and you will too.